Broken link building is a powerful white‑hat SEO tactic where you help site owners fix dead links and earn high‑quality backlinks in return. When used systematically, it can become a consistent, compounding source of authority and organic traffic for your site.
What is broken link building?
Broken link building means finding links on other websites that point to 404 pages, creating or offering a relevant replacement on your own site, and persuading the site owner to swap their dead link for your working resource. Because you solve a real usability problem (a broken reference), this method is considered a white‑hat way to build links.
![Broken link building flow]
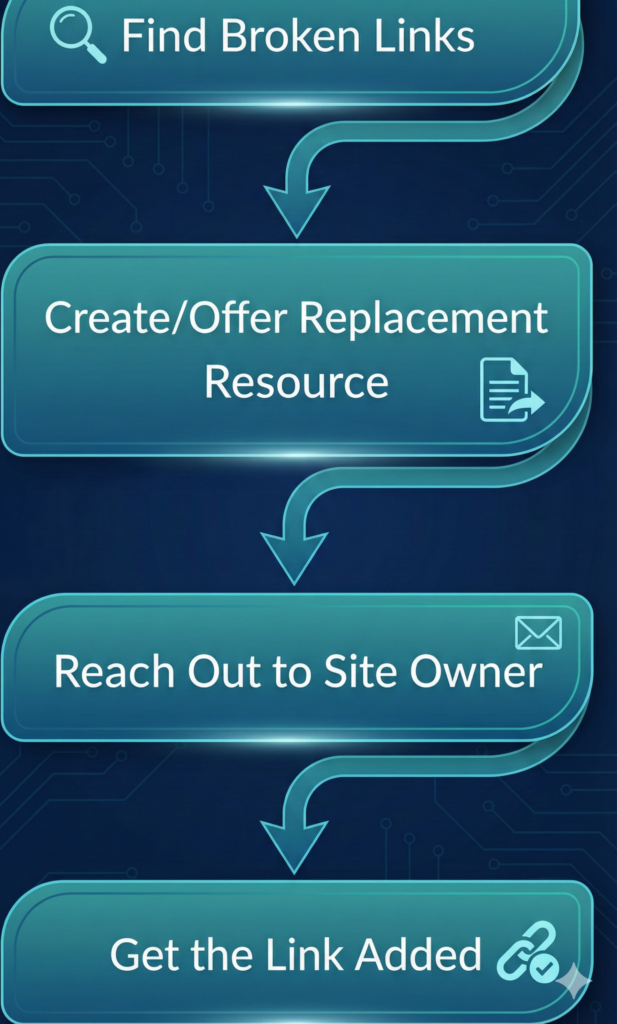
Overview of the broken link building process
- A “broken” or “dead” link typically leads to a 404 error because the target page was deleted, moved without a redirect, or the URL was mistyped.
- The basic process: find broken links in your niche, create a similar or better resource, then run outreach to have your URL added instead.
Why does it work so well?
Broken link building works because it aligns incentives: you improve the webmaster’s page while gaining a relevant backlink for yourself. Unlike generic link requests, you lead with a concrete fix to a visible problem, which dramatically raises response and placement rates.
- Broken links harm user experience and can negatively impact SEO signals on large or important pages, so many site owners are motivated to fix them.
- When your content closely matches the original topic, swapping the dead URL for yours is an easy, low‑risk decision for the webmaster.

Best practices
Use Check My Links
Check My Links is a Chrome extension that scans any page and highlights live and broken links so you can quickly spot opportunities. It colors‑codes links (valid vs. 404) and lets you export or copy URLs, making it ideal for link pages, resource lists, and long blog posts.
- Use Google to find “resources” or “links” pages in your niche (e.g., “email marketing resources”), open them, and run Check My Links to surface dead outbound links.
- Prioritize pages with many external links, since each broken URL there can reveal multiple domains linking to that same dead page.
Find pages with lots of links
The best broken link prospects are pages that already attract many external links, like resource hubs, glossary pages, and definitive guides. If a heavily cited page goes offline, every site still linking to it becomes a warm prospect for your outreach.
- Use queries like “keyword + resources”, “keyword + links”, or “keyword + recommended tools” to discover curated pages in your industry.
- Once you find a promising resource page, scan it with a broken‑link checker (browser extension or SaaS tool) and log every dead outbound URL and its anchor text.
Wikipedia “dead link” technique
Wikipedia is full of dead citations marked with “dead link” tags, and those references usually have many external links pointing to the same now‑defunct page. This makes Wikipedia a high‑leverage discovery engine for broken link campaigns in almost any niche.
![Wikipedia dead link process]
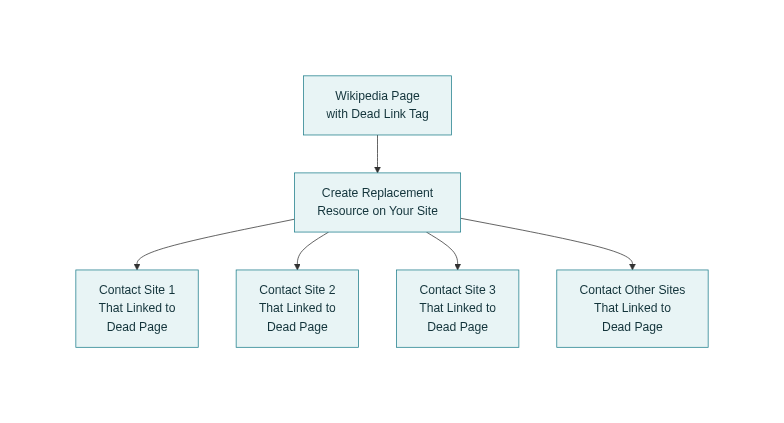
How the Wikipedia dead link technique works
- Use Google operators like site:wikipedia.org “dead link” [your niche] to find relevant articles with dead citations you could potentially replace.
- Then use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or similar to find all sites still linking to that dead URL, creating a prospect list for your outreach.
Two Semrush features that help
Semrush offers multiple features built specifically to speed up broken link building workflows.
- Backlink Analytics → Indexed Pages → Broken pages: Enter a competitor’s domain, then filter for “Broken pages” to discover their dead URLs that still attract backlinks.
- Backlink Analytics / Backlink Gap: Find external domains linking to those broken competitor pages so you can recreate similar content and contact the same sites with a replacement.
Semrush can also surface broken internal/external links via Site Audit, helping you reclaim lost link equity on your own site while you build new links.
Offer a very close replacement
Your replacement should closely match the original topic, scope, and intent of the dead content so it feels like a natural swap. When the anchor text and your new page align tightly (e.g., same subject, similar promise), webmasters rarely worry about relevance or quality mismatch.
- Study the old URL in a cached copy or using archive services to understand what people originally linked to (definition, guide, stats, etc.).
- Mirror the core angle and structure, but update data, improve clarity, and add missing sections so your replacement feels like an upgrade, not a clone.
Recreate dead content
For high‑value broken pages with lots of quality backlinks, fully recreating the content on your site can be worth the extra effort. This “1:1 plus improvements” approach often delivers excellent conversion rates from outreach because you restore exactly what everyone wanted to reference.
- Use archive snapshots (when available) to map all major sections, examples, and references, then rebuild them in a modernized, original way.
- Keep URLs clean, structure logical, and on‑page SEO tight so that once links are reclaimed, the new page can also rank and drive ongoing traffic.
Be super helpful in your outreach
Effective broken link outreach emails are short, polite, and genuinely helpful, highlighting the exact broken URL and your suggested replacement. The tone should focus on fixing a problem for the webmaster first, with your link as the obvious solution.
- Mention the broken link location (page URL, section, or anchor) and explain how it affects their readers’ experience.
- Provide your replacement link in a simple, skimmable way and thank them for the resource page or article so the message feels personalized and human.
Find the right person
Sending emails to generic addresses or contact forms can work, but targeting the actual owner or editor raises success rates dramatically. In many cases, you can locate the right person via the site’s “About” section, author bio, or LinkedIn.
- Look for roles like editor, content manager, SEO manager, or webmaster; these people usually control external links and content updates.
- Keep subject lines specific (e.g., “Broken link on your [guide title]”) so the recipient instantly understands the value of opening your email.
Don’t be a pushy jerkface
Aggressive follow‑ups or entitled language will quickly burn relationships and damage your brand, even if the opportunity looks tempting. Broken link building works long‑term only if you maintain goodwill and respect site owners’ time and decisions.
- Limit follow‑ups (for example, one or two gentle reminders spaced a few days apart), and stop completely if there is no response.
- Avoid ultimatums, guilt‑tripping, or over‑selling; a calm reminder that you noticed a broken reference and can help is usually enough.
Skip over dead sites
Not every broken link is worth chasing—some sites are outdated, abandoned, or spammy, and their links may provide little or no SEO value. Focusing on high‑quality, active domains keeps your efforts efficient and your backlink profile clean.
- Quickly review each prospect’s recent publishing activity, domain quality, and topical relevance before adding them to your outreach list.
- Ignore sites with low trust, thin content, or obvious link manipulation patterns to protect your site’s reputation and rankings.
Learn more
Once the basics are in place, broken link building can be scaled into a repeatable acquisition channel supported by tools and templates. Advanced guides from specialist link building agencies and SEO platforms walk through prospecting at scale, automation, and team workflows.
- Explore in‑depth broken link building guides from major SEO blogs (Ahrefs, Semrush, LinkBuilder, etc.) to refine your process and scripts.
- Combine broken link building with other tactics like digital PR, guest posting, and content hubs to create a diversified, resilient off‑page strategy.